Air purification device
An air purification device can capture or partially or completely destroy pollutants from indoor air.
The major pollutant categories are:
- Breathable particles suspended in the air
- Gaseous pollutants (chemical detergents, solvents, compounds from building materials, etc.)
- Microorganisms (bacteria and mould)
- Allergens (animal hair, pollen, etc.)
There are devices that can be used in the residential or commercial sector (offices, waiting room, retail stores, etc.) combining one or more technologies depending on the type of purification sought.
Working principle
The technologies used for air purification vary from one model to another according to the manufacturers. They currently include:
- Filter
Captures suspended particles, hair, pollen and other allergens. - HEPA filter
Captures fine particles - Activated carbon filters
Absorbs gases, odours, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) (chemical detergents and solvents) - Photocatalysis
Photocatalysis destroys organic and chemical pollution and bad odours in the air at room temperature and without addition of compounds, to transform them into water vapour and carbon dioxide when the reaction is complete. - Ioniser
Generates negative ions that amalgamate suspended particles. The amalgamated particles, too heavy to stay in the air, fall to the ground. - UV lamp
Destroys germs and bacteria in the air. - Plasma
The plasma air purifiers (excited gas) act by exciting the oxygen and generate an oxidising molecule that is forced into the room to clean the air. Air is therefore purified not in the device but on the outside. This process is effective on microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses, and volatile organic compounds. A major disadvantage is that this kind of air purification device loads the air with ozone and other free radicals (singlet oxygen, hydroxyl, peroxide, etc.), which are toxic for organisms, causing respiratory tract lesions even at low concentrations; the reaction also emits an odour. This kind of air purification device should therefore not be used in permanently inhabited environments. It has a rather industrial application.
Benefits of an air purification device
- Reduced suspended particles, VOCs, bacteria/viruses, mould
- Improved health: Reduction of problems related to allergies, asthma.
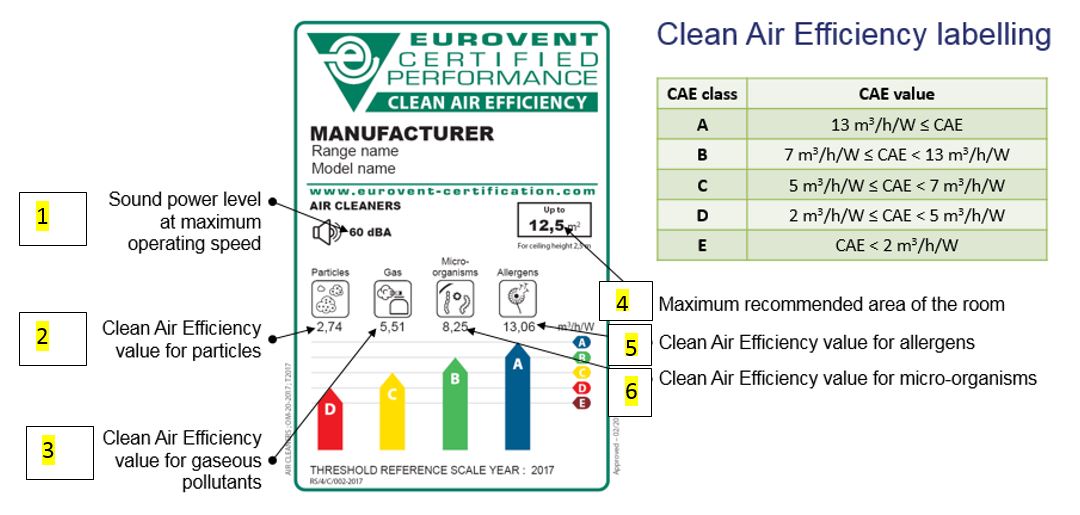
An air filtration efficiency label
This label is currently used for products with Eurovent Certified Performance. It is not available for NF mark certified products.
Compare to make the right choice
It is very easy to make the right choice: just compare the products. But when product performance is not certified, this becomes impossible.
Certification makes it possible to compare objectively.
- The product performance is evaluated according to the same criteria, and the results are expressed in the same unit of measurement, regardless of the country where the products are manufactured or marketed.
- A certified product has its performance verified by an impartial, independent and competent accredited body.
- Certified products comply with standards.
- A product whose performance is certified will work according to the specifications stated by the manufacturer.
The performance we certify
- Air flow (50 m3/h) = ability to absorb and purify a quantity of air in relation to a room volume
- Sound Power (dB) = sound that the device makes during operation
- Electric power (kW/h) = electricity consumption
Related technical insights
 Ventilation & indoor air quality for homes
Ventilation & indoor air quality for homes
NF Air cleaners
 Ventilation & indoor air quality for homes
Ventilation & indoor air quality for homes